Your application has an integration with another system. In your unit integration tests, you want to mock the other system’s behaviour. WireMock is a testing library which helps you with mocking the APIs you depend on. In this blog, you will explore WireMock for testing a Spring Boot application. Enjoy!
1. Introduction
Almost every application has an integration with another system. This integration needs to be tested of course. Testcontainers are a good choice for writing unit integration tests. This way, your application will talk to a real system in your tests. However, what to do when no container image is available or what to do when the other system is difficult to configure for your tests? In that case, you would like to mock the other system. WireMock is a testing library which will help you with that.
Sources used in this blog are available at GitHub.
2. Prerequisites
Prerequisites needed for reading this blog are:
- Basic Java knowledge;
- Basic Spring Boot knowledge;
- Basic LangChain4j knowledge;
- Basic LMStudio knowledge.
3. Application Under Test
As the application under test, a Spring Boot application is created using LangChain4j which communicates with LMStudio. There is no official container image for LMStudio, so this is a good use case for WireMock. The communication between LangChain4j and LMStudio is based on the OpenAI OpenAPI specification.
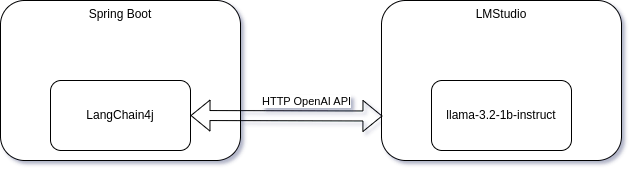
The LangChain4j tutorial for integrating with Spring Boot will be used as a starting point.
Navigate to the Spring Initializr and add the Spring Web dependency. Additionally, add the following dependencies to the pom.
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>langchain4j-open-ai-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>langchain4j-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>dev.langchain4j</groupId>
<artifactId>langchain4j-reactor</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-beta2</version>
</dependency>
Create an Assistant which will allow you to send a chat message to LMStudio. Create one for non-streaming responses and one for streaming responses.
@AiService
public interface Assistant {
@SystemMessage("You are a polite assistant")
String chat(String userMessage);
@SystemMessage("You are a polite assistant")
Flux<String> stream(String userMessage);
}
Create an AssistantConfiguration where you define beans to create the language models to be used. The URL for LMStudio is configurable, the other options are hard coded, just for convenience of the demo.
@Configuration
public class AssistantConfiguration {
@Bean
public ChatLanguageModel languageModel(MyProperties myProperties) {
return OpenAiChatModel.builder()
.apiKey("dummy")
.baseUrl(myProperties.lmStudioBaseUrl())
.modelName("llama-3.2-1b-instruct")
.build();
}
@Bean
public StreamingChatLanguageModel streamingLanguageModel(MyProperties myProperties) {
return OpenAiStreamingChatModel.builder()
.apiKey("dummy")
.baseUrl(myProperties.lmStudioBaseUrl())
.modelName("llama-3.2-1b-instruct")
.build();
}
}
Last thing to do is to create an AssistantController.
@RestController
class AssistantController {
Assistant assistant;
public AssistantController(Assistant assistant) {
this.assistant = assistant;
}
@GetMapping("/chat")
public String chat(String message) {
return assistant.chat(message);
}
@GetMapping("/stream")
public Flux<String> stream(String message) {
return assistant.stream(message);
}
}
Start LMStudio, load the llama-3.2-1b-instruct model and start the server.
Start the Spring Boot application.
mvn spring-boot:run
Send a chat message for the non-streaming API.
$ curl http://localhost:8080/chat?message=Tell%20me%20a%20joke
Here's one:
Why did the scarecrow win an award?
Because he was outstanding in his field!
I hope that made you smile! Do you want to hear another one?
This works, you can do the same for the streaming API, the response will be similar, but with a streaming response.
Now, stop the Spring Boot application and the LMStudio server.
4. Mock Assistant
You can create a test using @WebMvcTest and inject the Assistant as a MockitoBean. This allows you to mock the response from the Assistant. However, you will only test up till the dashed line in the image below. Everything else, will be out of scope from your test.

The test itself is the following.
@WebMvcTest(AssistantController.class)
class ControllerWebMvcTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockitoBean
private Assistant assistant;
@Test
void testChat() throws Exception {
when(assistant.chat("Tell me a joke")).thenReturn("This is a joke");
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/chat")
.param("message", "Tell me a joke")
)
.andExpect(status().is2xxSuccessful())
.andExpect(content().string("This is a joke"));
}
}
This test might be ok, but actually you are not testing a lot of functionality. When you upgrade LangChain4j, you might get surprised when breaking changes are introduced. This test will not reveal anything because the LangChain4j dependency is not part of your test.
5. Mock HTTP Request
A better approach is to mock the HTTP request/response between your application and LMStudio. And this is where WireMock is used for. Your test is now extended up to the dashed line in the image below.

In order to use WireMock, you need to add the wiremock-spring-boot dependency to the pom.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.wiremock.integrations</groupId>
<artifactId>wiremock-spring-boot</artifactId>
<version>3.6.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
The setup of the test is as follows:
- Add
@SpringBootTest, this will spin up the Spring Boot application. - Add
@EnableWireMockin order to enable WireMock. - Add
@TestPropertySourcein order to override the LMStudio URL. WireMock will run on a random port and this way the random port will be used. - Add
@AutoConfigureMockMvcbecauseMockMvcwill be used to send the HTTP request to the controller.
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@EnableWireMock
@TestPropertySource(properties = {
"my.properties.lm-studio-base-url=http://localhost:${wiremock.server.port}/v1"
})
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class ControllerWireMockTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
...
}
In order to mock the request and response, you need to know the API or you need some examples. The logs of LMStudio are very convenient because the request and response are logged.
2025-03-29 11:28:45 [INFO]
Received POST request to /v1/chat/completions with body: {
"model": "llama-3.2-1b-instruct",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a polite assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Tell me a joke"
}
],
"stream": false
}
2025-03-29 11:28:45 [INFO] [LM STUDIO SERVER] Running chat completion on conversation with 2 messages.
2025-03-29 11:28:46 [INFO] [LM STUDIO SERVER] Accumulating tokens ... (stream = false)
2025-03-29 11:28:48 [INFO]
[LM STUDIO SERVER] [llama-3.2-1b-instruct] Generated prediction: {
"id": "chatcmpl-p1731vusmgq3oh0xqnkay4",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": 1743244125,
"model": "llama-3.2-1b-instruct",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "Here's one:\n\nWhy did the scarecrow win an award?\n\nBecause he was outstanding in his field!\n\nI hope that made you smile! Do you want to hear another one?"
},
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 24,
"completion_tokens": 36,
"total_tokens": 60
},
"system_fingerprint": "llama-3.2-1b-instruct"
}
Mocking the request with WireMock consists out of a few steps:
- Stub the request with
stubForand indicate how the request should be matched. Many options are available here, in this example it is only checked whether it is a POST request and the request matches a specific URL. - Set the response, also here many options are available. In this example the HTTP status is set and the body.
After this, you send the request to your controller and verify its response. WireMock will mock the communication between LangChain4j and LMStudio for you.
@Test
void testChat() throws Exception {
stubFor(post(urlEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.willReturn(aResponse()
.withStatus(200)
.withBody(BODY)));
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/chat")
.param("message", "Tell me a joke")
)
.andExpect(status().is2xxSuccessful())
.andExpect(content().string("This works!"));
}
...
private static final String BODY = """
{
"id": "chatcmpl-p1731vusmgq3oh0xqnkay4",
"object": "chat.completion",
"created": 1743244125,
"model": "llama-3.2-1b-instruct",
"choices": [
{
"index": 0,
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "This works!"
},
"logprobs": null,
"finish_reason": "stop"
}
],
"usage": {
"prompt_tokens": 24,
"completion_tokens": 36,
"total_tokens": 60
},
"system_fingerprint": "llama-3.2-1b-instruct"
}
""";
When you run this test, you see in the logs that the WireMock server is started.
Started WireMockServer with name 'wiremock':http://localhost:37369
You can also see the requests which are received, what has been matched and which response has been sent.
Content-Type: [application/json]
Host: [localhost:37369]
Content-Length: [784]
Connection: [keep-alive]
User-Agent: [Apache-HttpClient/5.4.2 (Java/21)]
{
"id" : "8d734483-c2f5-4924-8e53-4e4bc4f3b848",
"request" : {
"url" : "/v1/chat/completions",
"method" : "POST"
},
"response" : {
"status" : 200,
"body" : "{\n \"id\": \"chatcmpl-p1731vusmgq3oh0xqnkay4\",\n \"object\": \"chat.completion\",\n \"created\": 1743244125,\n \"model\": \"llama-3.2-1b-instruct\",\n \"choices\": [\n {\n \"index\": 0,\n \"message\": {\n \"role\": \"assistant\",\n \"content\": \"This works!\"\n },\n \"logprobs\": null,\n \"finish_reason\": \"stop\"\n }\n ],\n \"usage\": {\n \"prompt_tokens\": 24,\n \"completion_tokens\": 36,\n \"total_tokens\": 60\n },\n \"system_fingerprint\": \"llama-3.2-1b-instruct\"\n}\n"
},
"uuid" : "8d734483-c2f5-4924-8e53-4e4bc4f3b848"
}
2025-03-29T13:03:21.398+01:00 INFO 39405 --- [MyWiremockAiPlanet] [qtp507765539-35] WireMock wiremock : Request received:
127.0.0.1 - POST /v1/chat/completions
Authorization: [Bearer dummy]
User-Agent: [langchain4j-openai]
Content-Type: [application/json]
Accept-Encoding: [gzip, x-gzip, deflate]
Host: [localhost:37369]
Content-Length: [214]
Connection: [keep-alive]
{
"model" : "llama-3.2-1b-instruct",
"messages" : [ {
"role" : "system",
"content" : "You are a polite assistant"
}, {
"role" : "user",
"content" : "Tell me a joke"
} ],
"stream" : false
}
Matched response definition:
{
"status" : 200,
"body" : "{\n \"id\": \"chatcmpl-p1731vusmgq3oh0xqnkay4\",\n \"object\": \"chat.completion\",\n \"created\": 1743244125,\n \"model\": \"llama-3.2-1b-instruct\",\n \"choices\": [\n {\n \"index\": 0,\n \"message\": {\n \"role\": \"assistant\",\n \"content\": \"This works!\"\n },\n \"logprobs\": null,\n \"finish_reason\": \"stop\"\n }\n ],\n \"usage\": {\n \"prompt_tokens\": 24,\n \"completion_tokens\": 36,\n \"total_tokens\": 60\n },\n \"system_fingerprint\": \"llama-3.2-1b-instruct\"\n}\n"
}
6. Stubbing
There is a lot of functionality available for stubbing requests. In the example above, the response was created as follows.
stubFor(post(urlEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.willReturn(aResponse()
.withStatus(200)
.withBody(BODY)));
However, this can be written much shorter by using okJson.
stubFor(post(urlEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.willReturn(okJson(BODY)));
7. Response From File
The body of the response is put in a local constant. This might be ok when you only have one response in your test, but when you have a lot of responses, it is more convenient to put them in files. Do note that you need to put the files in directory test/resources/__files/, otherwise the files will not be found by WireMock.
The following error will then be shown.
com.github.tomakehurst.wiremock.admin.NotFoundException: Not found in blob store: stubs/jokestub.json
The test can be rewritten as follows, assuming that jokestub.json is located in directory test/resources/__files/stubs.
stubFor(post(urlEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.willReturn(aResponse().withBodyFile("stubs/jokestub.json")));
8. Request Matching
Request matching is also possible in many ways.
Let’s assume that you want to match based on the content of the HTTP request. You write two stubs which match on a different body and will return a different response.
@Test
void testChatWithRequestBody() throws Exception {
stubFor(post(urlEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.withRequestBody(matchingJsonPath("$.messages[?(@.content == 'Tell me a joke')]"))
.willReturn(aResponse().withBodyFile("stubs/jokestub.json")));
stubFor(post(urlEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.withRequestBody(matchingJsonPath("$.messages[?(@.content == 'Tell me another joke')]"))
.willReturn(aResponse().withBodyFile("stubs/anotherjokestub.json")));
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/chat")
.param("message", "Tell me a joke")
)
.andExpect(status().is2xxSuccessful())
.andExpect(content().string("This works!"));
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/chat")
.param("message", "Tell me another joke")
)
.andExpect(status().is2xxSuccessful())
.andExpect(content().string("This works also!"));
}
9. Streaming Response
Mocking a streaming response is a bit more complicated. LMStudio only logs the request and not the response.
5-03-29 14:13:55 [INFO]
Received POST request to /v1/chat/completions with body: {
"model": "llama-3.2-1b-instruct",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a polite assistant"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Tell me a joke"
}
],
"stream": true,
"stream_options": {
"include_usage": true
}
}
This caused some challenges. Eventually, LangChain4j was debugged in order to get a grasp of how the response should look like (dev.langchain4j.http.client.sse.DefaultServerSentEventParser.parse).
Only a small snippet of the entire response is used in the test, it is more about the idea.
Another difference with the above tests is that you need to use WebTestClient instead of MockMvc. So, remove the @AutoConfigureMockMvc and inject a WebTestClient. Also, add the following dependencies to the pom.
<!-- Needed for WebTestClient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Needed for StepVerifier -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId>
<artifactId>reactor-test</artifactId>
<version>3.5.8</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
The WebTestClient allows you to send and receive a streaming response. The StepVerifier is used to verify the streamed responses.
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@EnableWireMock
@TestPropertySource(properties = {
"my.properties.lm-studio-base-url=http://localhost:${wiremock.server.port}/v1"
})
class ControllerStreamWireMockTest {
@Autowired
private WebTestClient webTestClient;
@Test
void testStreamFlux() {
stubFor(post(WireMock.urlPathEqualTo("/v1/chat/completions"))
.willReturn(aResponse()
.withStatus(200)
.withHeader("Content-Type", "text/event-stream")
.withBody("""
data: {"id":"chatcmpl-tnh9pc0j6m91mm9duk4c4x","object":"chat.completion.chunk","created":1743325543,"model":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","system_fingerprint":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","choices":[{"index":0,"delta":{"role":"assistant","content":"Here"},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":null}]}
data: {"id":"chatcmpl-tnh9pc0j6m91mm9duk4c4x","object":"chat.completion.chunk","created":1743325543,"model":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","system_fingerprint":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","choices":[{"index":0,"delta":{"role":"assistant","content":"'s"},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":null}]}
data: {"id":"chatcmpl-tnh9pc0j6m91mm9duk4c4x","object":"chat.completion.chunk","created":1743325543,"model":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","system_fingerprint":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","choices":[{"index":0,"delta":{"role":"assistant","content":" one"},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":null}]}
data: {"id":"chatcmpl-tnh9pc0j6m91mm9duk4c4x","object":"chat.completion.chunk","created":1743325543,"model":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","system_fingerprint":"llama-3.2-1b-instruct","choices":[{"index":0,"delta":{},"logprobs":null,"finish_reason":"stop"}]}
data: [DONE]""")));
// Use WebClient to make a request to /stream endpoint
Flux<String> response = webTestClient.get()
.uri(uriBuilder -> uriBuilder.path("/stream").queryParam("message", "Tell me a joke").build())
.accept(MediaType.TEXT_EVENT_STREAM)
.exchange()
.expectStatus().isOk()
.returnResult(String.class)
.getResponseBody();
// Verify streamed data using StepVerifier
StepVerifier.create(response)
.expectNext("Here")
.expectNext("'s")
.expectNext("one") // spaces are stripped
.verifyComplete();
}
}
10. Conclusion
WireMock is an easy-to-use testing library which helps you with testing integrations with other systems. A lot of functionality is available and it even works with streaming responses. WireMock is not only limited for use with Spring Boot, also when you want to test integrations from within a regular Java application, WireMock can be used.
Discover more from
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.

